L’acné : Comprendre et traiter cette affection cutanée
L’acné est une affection courante de la peau qui touche principalement les adolescents, mais elle peut également affecter les adultes. Elle se manifeste par l’apparition de boutons, de points noirs et de kystes principalement sur le visage, le dos et la poitrine. L’acné peut avoir des impacts significatifs sur la qualité de vie et l’estime de soi des personnes affectées.
L'approche unique Clinique M
À la Clinique M Rockland, nous comprenons que chaque peau est différente. Notre approche combine une expertise médicale reconnue, des technologies de pointe et des protocoles personnalisés afin de traiter efficacement l’acné active et ses cicatrices.
Que ce soit par nos peelings spécialisés, le Hollywood Peel, le microneedling RF Potenza ou encore nos soins sur mesure, nous visons non seulement à améliorer l’apparence de la peau, mais aussi à redonner confiance et confort à nos patients.

L’acné à différents âges
Consultation gratuite
L’acné chez les adolescents
Causes
Chez les adolescents, l’acné est principalement causée par les changements hormonaux associés à la puberté. Les androgènes stimulent les glandes sébacées, entraînant une production excessive de sébum et une obstruction des pores.
Symptômes
Les adolescents développent souvent des comédons (points noirs et blancs), des papules, des pustules, et dans certains cas, des nodules et kystes sur le visage, le dos et la poitrine.
L’acné chez les adultes
Causes
Chez les adultes, les causes de l’acné peuvent inclure des fluctuations hormonales, le stress, certains médicaments, et des produits cosmétiques comédogènes. Les femmes peuvent également être affectées par des conditions hormonales telles que le syndrome des ovaires polykystiques (SOPK).
Symptômes
Les adultes peuvent développer des lésions similaires à celles des adolescents, mais l’acné tend à persister plus longtemps et à se concentrer davantage sur la mâchoire et le menton.
L’acné chez les Personnes Âgées
Causes
Chez les personnes âgées, l’acné est moins fréquente mais peut être causée par des facteurs hormonaux, certains médicaments, et des problèmes de santé sous-jacents. La peau vieillissante peut également réagir différemment aux traitements.
Symptômes
Les symptômes peuvent inclure des papules, pustules, et parfois des nodules. La peau plus mature peut être plus sensible et plus sujette aux irritations.
Les causes de l’acné

Liens rapides
Consultation gratuite
Les mécanismes de l’acné
L’acné est le résultat de plusieurs processus biologiques interdépendants. Les principaux mécanismes impliqués sont :
Production excessive de sébum
Les glandes sébacées produisent du sébum pour lubrifier et protéger la peau. Cependant, une production excessive peut conduire à l’obstruction des follicules pileux.
Hyperkératinisation
Ce processus se réfère à une augmentation de la production de cellules cutanées mortes à l’intérieur des follicules pileux. Ces cellules mortes, combinées au sébum, formant des bouchons qui obstruent les pores.
Prolifération de bactéries
La bactérie Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) prospère dans les pores obstrués et se nourrit de sébum. Sa prolifération peut provoquer une réponse inflammatoire du système immunitaire.
Inflammation
L’inflammation est une réponse du système immunitaire à la prolifération de P. acnes et à la rupture des parois des follicules. Cela entraîne la formation de lésions inflammatoires telles que les papules, pustules, nodules et kystes.
Facteurs contributifs
Plusieurs facteurs peuvent contribuer à l’apparition et à l’aggravation de l’acné. Voici les principaux :
Fluctuations hormonales
Les changements hormonaux, notamment ceux liés à la puberté, aux cycles menstruels, à la grossesse et à certaines conditions médicales (comme le syndrome des ovaires polykystiques), peuvent stimuler les glandes sébacées et augmenter la production de sébum.
Génétique
L’acné peut avoir une composante héréditaire. Les personnes ayant des antécédents familiaux d’acné sont plus susceptibles de développer cette condition.
Alimentation
Bien que les preuves ne soient pas définitives, certains aliments riches en glucides, les produits laitiers, et les aliments à indice glycémique élevé peuvent exacerber l’acné chez certaines personnes. Pour des conseils sur l’alimentation et l’acné, visitez Diabète Canada.
Produits cosmétiques et soins de la peau
L’utilisation de produits comédogènes (qui obstruent les pores) peut aggraver l’acné. Il est important d’utiliser des produits non comédogènes et adaptés à son type de peau.
Médicaments
Certains médicaments, comme les corticostéroïdes, les anticonvulsivants, et certains contraceptifs oraux, peuvent provoquer ou aggraver l’acné.
Stress
Le stress ne cause pas directement l’acné, mais il peut aggraver les symptômes en influençant les niveaux hormonaux et en perturbant les comportements de soin de la peau. Pour plus d’informations sur la gestion du stress, consultez la Société canadienne de psychologie.
Facteurs environnementaux
Les conditions environnementales peuvent également jouer un rôle dans le développement et l’aggravation de l’acné. Voici quelques exemples :
Climat et humidité
Les climats chauds et humides peuvent augmenter la production de sébum et favoriser l’obstruction des pores.
Pollution
L’exposition à la pollution et à d’autres irritants environnementaux peut enflammer la peau et aggraver les symptômes de l’acné. Pour plus d’informations sur les impacts environnementaux sur la santé de la peau, visitez Environnement et Changement climatique Canada.
Hygiène et habitudes de vie
Une mauvaise hygiène, comme ne pas se laver le visage régulièrement ou utiliser des outils de maquillage sales, peut contribuer à l’obstruction des pores. De même, une alimentation déséquilibrée et un manque d’exercice peuvent influencer la santé de la peau.

Les mythes sur les causes de l’acné
Il existe de nombreux mythes concernant les causes de l’acné. Il est important de distinguer les faits des idées reçues :
Alimentation
Contrairement à la croyance populaire, les aliments gras et le chocolat ne causent pas directement l’acné. Toutefois, une alimentation équilibrée peut aider à maintenir une peau saine.
Hygiène
L’acné n’est pas causée par une mauvaise hygiène. En fait, un nettoyage excessif peut irriter la peau et aggraver les symptômes.
Soleil
Bien que l’exposition au soleil puisse temporairement améliorer les symptômes de l’acné, elle peut également causer des dommages à long terme et aggraver l’acné avec le temps.
Classification de la sévérité de l’acné
L’acné est classée en fonction de sa gravité pour déterminer le traitement approprié. Voici les catégories généralement utilisées :
Acné légère
Présence de comédons ouverts (points noirs) et fermés (points blancs) avec quelques papules et pustules. L’atteinte est généralement limitée au visage.
Acné modérée
De nombreux comédons, papules et pustules, avec possibilité de quelques nodules. L’atteinte peut s’étendre au dos et à la poitrine.
Acné sévère
Présence de nombreux nodules et kystes douloureux, souvent associés à une inflammation significative. Le risque de cicatrices permanentes est élevé.
Mesures d’hygiène et pratiques de vie pour gérer l’acné
Consultation gratuite
Pratiques à Éviter
Certaines pratiques peuvent aggraver l’acné. Voici ce qu’il faut éviter :
Ne pas manipuler les boutons
Éviter de presser, gratter ou manipuler les boutons, car cela peut provoquer une inflammation, des infections et des cicatrices.
Éviter les produits comédogènes
Choisir des produits de soins et de maquillage étiquetés “non comédogènes” pour prévenir l’obstruction des pores.
Ne pas trop se laver le visage
Un nettoyage excessif peut irriter la peau et stimuler la production de sébum. Limiter le nettoyage à deux fois par jour.
Hygiène de vie
Certaines habitudes de vie peuvent aider à gérer l’acné. Voici quelques conseils :
Alimentation équilibrée
Adopter une alimentation riche en fruits, légumes, protéines maigres et grains entiers. Éviter les aliments riches en sucre et à indice glycémique élevé qui peuvent aggraver l’acné chez certaines personnes.
Hydratation
Boire suffisamment d’eau chaque jour pour maintenir une bonne hydratation de la peau.
Gestion du stress
Pratiquer des techniques de gestion du stress, telles que le yoga, la méditation ou la respiration profonde, pour éviter les poussées d’acné liées au stress.
Conseils spécifiques
Certaines situations nécessitent des précautions spécifiques pour gérer l’acné :
Activités sportives
Après une séance de sport, se doucher rapidement pour éliminer la sueur et éviter l’obstruction des pores. Utiliser des vêtements en matières respirantes.
Exposition au soleil
Utiliser une protection solaire non comédogène pour éviter les dommages cutanés. Bien que le soleil puisse temporairement améliorer l’acné, il peut aussi causer des effets néfastes à long terme.
Utilisation des cosmétiques
Limiter l’utilisation de cosmétiques lourds et opter pour des produits légers et non comédogènes. Nettoyer régulièrement les pinceaux et applicateurs de maquillage.
Importance de la consistance
La gestion de l’acné nécessite de la patience et de la constance. Il est essentiel de :
- Suivre une routine de soins régulière sans sauter d’étapes.
- Utiliser les traitements prescrits de manière continue, même si les résultats ne sont pas immédiatement visibles.
- Consulter régulièrement pour ajuster le traitement en fonction des progrès.
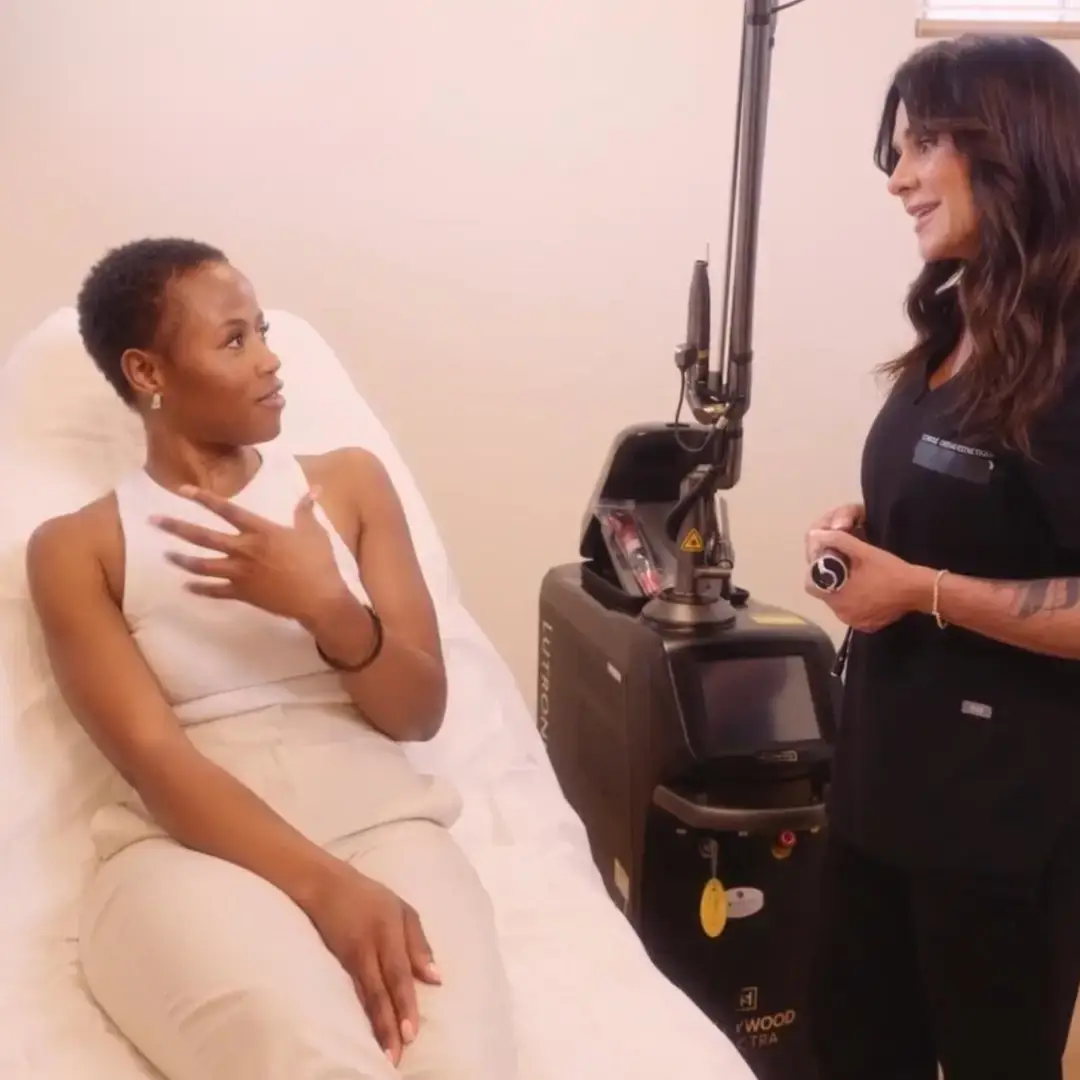
Solutions technologiques pour améliorer l’acné
Les traitements par laser sont utilisés pour cibler et traiter les différentes couches de la peau affectées par l’acné. Ils peuvent aider à réduire les cicatrices d’acné et à améliorer l’apparence générale de la peau.

Liens rapides
Consultation gratuite
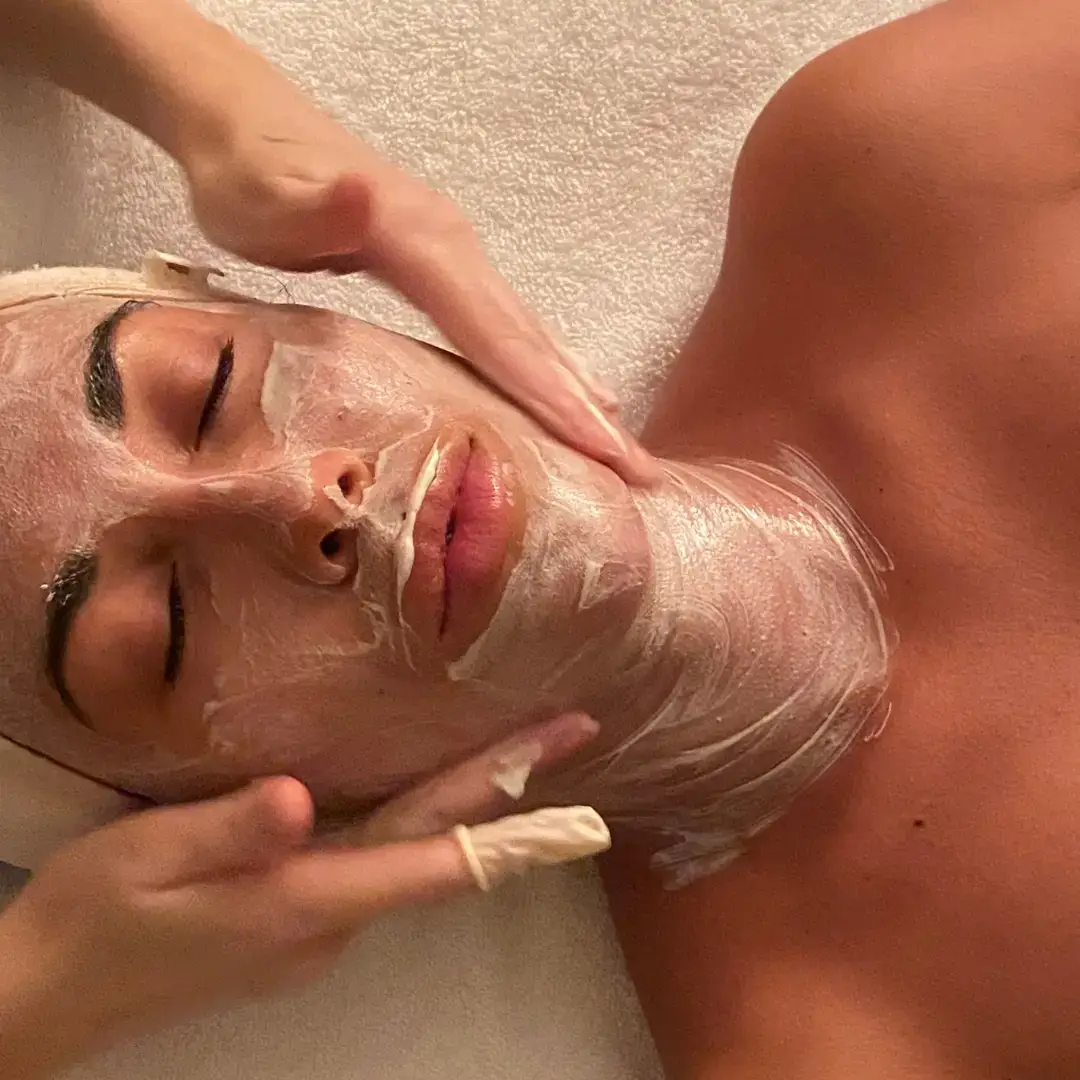
Hollywood Peel – Spectra
Un soin laser polyvalent qui purifie la peau et améliore visiblement son éclat. Grâce à une technologie unique combinant une lotion brevetée et une triple longueur d’onde, le Spectra™ réduit l’inflammation de l’acné, régule la production de sébum et stimule le renouvellement cellulaire. Résultat : une peau plus lisse, des pores resserrés et moins de poussées acnéiques.
Peeling chimiques
Nos peelings professionnels ciblent les imperfections laissées par l’acné : boutons, points noirs, cicatrices superficielles et taches pigmentaires. En éliminant les cellules mortes et en accélérant le renouvellement de la peau, ils favorisent une texture plus uniforme et un teint clarifié. Chaque peeling est adapté à votre type de peau pour des résultats sûrs et progressifs.
Laser fractionné
Une technologie avancée qui traite en profondeur les cicatrices d’acné et les irrégularités cutanées. Le laser fractionné stimule intensément la production de collagène, lisse la peau et atténue les marques persistantes. Dès les premières séances, les lésions actives diminuent, les cicatrices s’adoucissent et la peau retrouve une apparence plus homogène et saine.
Vitaminothérapie – Ionzyme DF II
Un traitement innovant qui utilise des courants galvaniques et des ondes sonores pour faire pénétrer en profondeur les vitamines essentielles et les antioxydants. Cette technologie stimule la régénération cellulaire, apaise l’inflammation et améliore la cicatrisation, ce qui en fait un allié de choix pour les peaux sujettes à l’acné et aux cicatrices. Résultat : une peau plus saine, plus résistante et visiblement revitalisée.
Produits de soins recommandés
Les traitements topiques sont appliqués directement sur la peau et sont souvent utilisés pour les formes légères à modérées d’acné.
Consultation gratuite
Nettoyants doux

Un nettoyant médicamenteux sans huile, au pH équilibré. Formulé avec 2% d’acide salicylique USP et de l’hexamidine, il élimine les bactéries, l’excès de sébum et nettoie les pores en profondeur.

Resserre l’apparence des pores et affine la texture de la peau pour la rendre visiblement plus lisse et plus douce. Anti-inflammatoire, antimicrobien et hypoallergénique.

Un masque purifiant luxueux à base d’argile rouge et blanche de Kaolin, aussi formulé avec des AHA pour exfolier les cellules mortes et déboucher les pores.
Crèmes/sérums contenant des ingrédients pour diminuer l’acné

Formulé avec de l’arbutine et du résorcinol pour stimuler le renouvellement cellulaire et éclaircir naturellement l’apparence des taches brunes due à l’acné.

Un gel hydratant innovant et léger à double action formulé avec de l’acide hyaluronique et des neuropeptides pour stimuler l’hydratation.

Une lotion efficace pour combattre l’acné et contrôler les imperfections, avec 5% de peroxyde de benzoyle, USP, qui élimine et prévient la formation de nouveaux boutons d’acné, de points noirs et de points blancs.
Protection solaire

Un écran solaire au fini mat et soyeux avec un FPS de 45 assurant une protection à large spectre contre les UVA et les UVB avec un effet matifiant.

Un écran solaire 100 % minéral avec un FPS de 30 assurant une protection à large spectre contre les UVA et les UVB qui procure un teint frais et éclatant.
Your transformation starts here
Do not hesitate to contact us for a personalized consultation and to begin your transformation.
* Results may vary from person to person. We present, to the best of our knowledge, an average of the results obtained. No guarantee is offered. Our goal is to properly evaluate your profile so that you can make an informed decision.
Get a free consultation*
Consultation without obligation
Thousands of satisfied clients have trusted our medical-aesthetic clinic for over 15 years.
Thousands of satisfied customers




A trusted medical-aesthetic clinic for over 15 years.
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ — 4.9/5 on Google
Our commitment
Response within 24 hours
Personalized treatment
Contact Us
Phone
(438) 601-4718
Our Address
233 Av. Dunbar, Mont-Royal, QC H3P 2H4, Canada