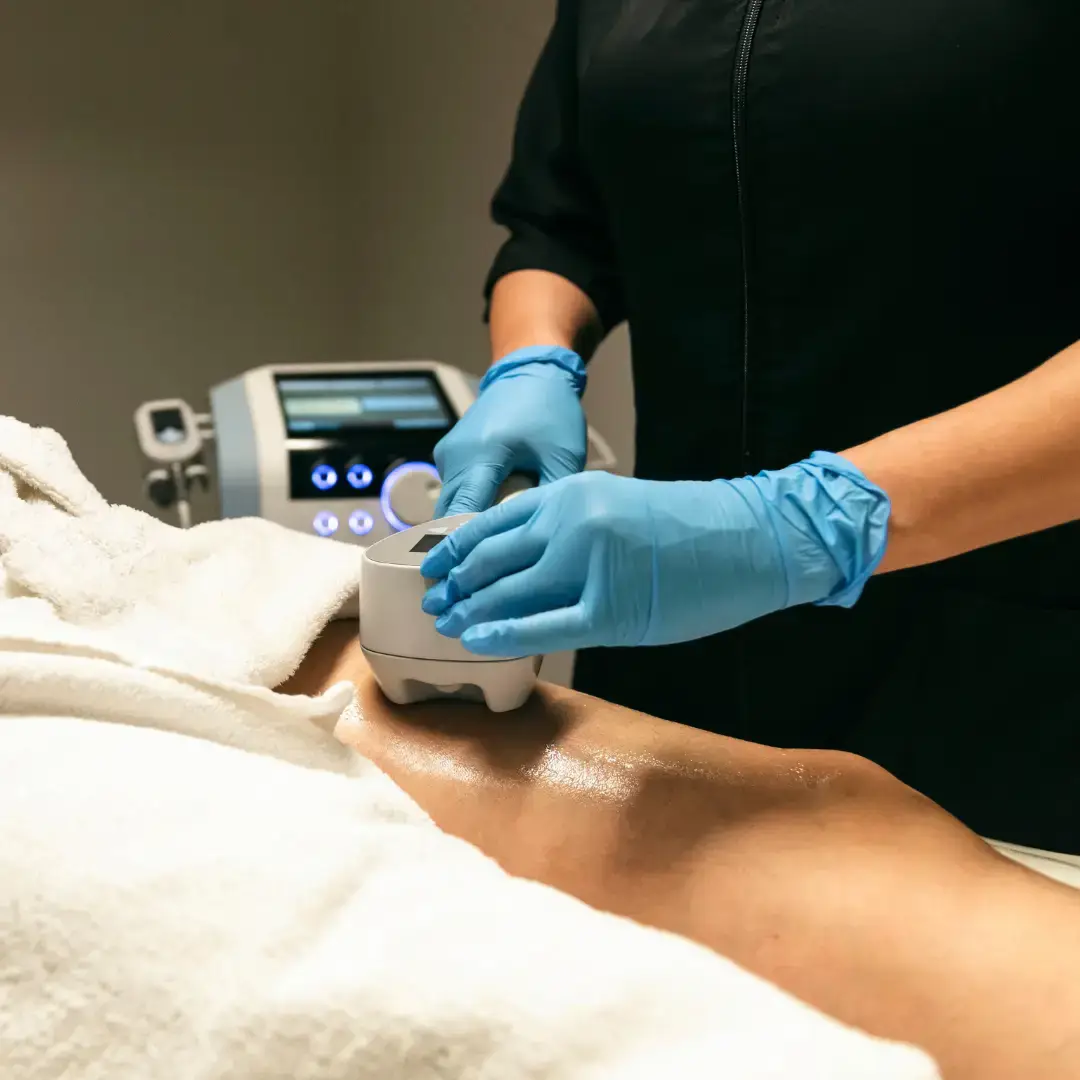
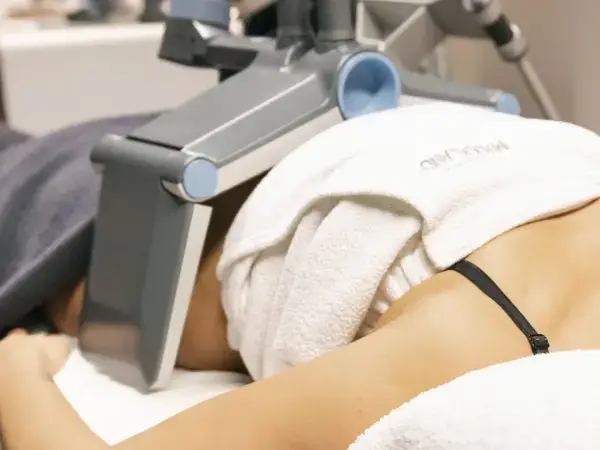
Fat loss
Understand and act effectively
Fat loss goes beyond simple weight loss. This profound body composition transformation requires a comprehensive understanding and an adapted approach for lasting and harmonious results.
The unique approach of Clinique M
At Clinique M, fat reduction is more than just aesthetics, it’s a complete transformation. With over 20 years of expertise and the most advanced technologies, we offer personalized protocols that combine safety, long-lasting results, and body harmony.
Recommended treatments
sur protocole complet (9 séances)
Body Fat: an essential element to understand
The mere mention of body fat often evokes a series of negative images. However, the reality is more nuanced: fat does not inherently carry a negative connotation, and several types of fat are essential for our health.
The vital role of adipose tissue
Adipose tissue, commonly called “fat,” plays a fundamental role in our bodies. It is involved in many essential metabolic processes:
- Energy production
- Regulation of body temperature
- Synthesis of certain hormones
- Protection of vital organs
Did you know?
The human body naturally produces the fats it needs. However, certain essential fats, such as omega-3s, must be obtained through diet. Excess intake forces the body to store the surplus in adipose tissue.
Classification of fats
Essential fats
These fats are indispensable for the proper functioning of the body. They are found:
- In muscles
- Au niveau du systaème nerveux
- They ensure crucial physiological functions necessary for our survival.
Non-essential fats
As the name suggests, these fats are not physiologically necessary for the body. These fats:
- Are not utilized by the body
- Form “unsightly bulges”
- Can negatively impact health
The different types of body fat
Beyond the classification of essential and non-essential fat, there are five distinct types of fat, each with its characteristics and impact on the body.
Quick links
Free consultation
Causes of fat accumulation
A multifactorial origin
Excessive fat accumulation results from the interaction of several factors, and understanding these factors is essential for effective prevention and management.

Quick links
Free consultation
Dietary factors
The impact of sugar
Excess sugar in our diet has direct consequences on fat storage:
- Saturation of glycogen reserves
- Automatic conversion into fat
- Storage in adipose tissue
The role of fatty acids
The process is complex but precise:
- Derived from lipid digestion
- Stored in adipocytes as triglycerides
- Form adipose tissue (fat mass)
- Concentrate under the skin and around digestive organs
The influence of alcohol
Alcohol significantly impacts fat metabolism:
- Accumulation of triglycerides in the liver
- Immediate combustion by the body
- Reduced use of sugars and fatty acids
- Promotes fat storage
Key point
Any consumption exceeding the body’s caloric needs promotes fat accumulation.
Psychological factors
Sleep and its impact
Insufficient sleep quality leads to:
- Increased abdominal fat
- Disruption of hunger-regulating hormones
- Metabolic imbalance
Chronic stress
The effects of stress are numerous:
- Increased cortisol production
- Elevated appetite
- Easier fat storage
- Preference for high-calorie comfort foods
Preventive solutions
- Practice stress management techniques
- Adopt meditation or yoga routines
- Prioritize relaxation periods
Areas affected by fat accumulation
Understanding the body’s map
Fat accumulation follows specific patterns influenced by various factors. This distribution varies significantly by gender and is strongly affected by hormones.
Free consultation
Distribution by gender
Female characteristics:
- Fat primarily accumulates around the hips
- Results in a “pear-shaped” silhouette
- Directly influenced by female hormones (estrogen)
Male characteristics:
- Fat is concentrated in the abdominal area
- It tends to form an “apple-shaped” silhouette
- Linked to male hormones
Specific zones and their causes
Arms and Chest
Fat storage in these areas is influenced by:
- Below-normal testosterone levels
- Hormonal fluctuations (androgens)
- Result: Visible swelling of the biceps and chest, unrelated to muscle growth
Shoulders and Hips
Fat accumulation in these regions is linked to:
- Insulin imbalance in the blood
- Excessive sugar consumption
- Conversion of sugar into stored fat
Abdomen
Abdominal fat is susceptible to:
- The stress hormone (cortisol)
- A sedentary lifestyle
- An unbalanced diet
- Note: This location is common to both men and women but is more frequent in men.
Hips and Thighs
This typically female distribution is due to:
- The influence of estrogen
- Genetic predisposition
- Cyclical hormonal variations
Key point
Dietary habits and lifestyle can significantly alter fat distribution, even though hormonal predisposition plays a significant role.
The consequences of excess fat
beyond aesthetic concerns
The impact of excessive body fat goes far beyond appearance, deeply affecting physical health and psychological well-being.
Free consultation
Impact on physical health
Cardiovascular complications
Excess fat significantly increases the risk of:
- Myocardial infarction (heart attack)
- Arrhythmias (irregular heartbeat)
- Strokes
- High blood pressure
- Heart failure
Metabolic complications
Disruptions in metabolism include:
- Insulin resistance
- Dyslipidemia (high harmful cholesterol levels)
- Hypothyroidism
- Type 2 diabetes
- Hyperuricemia (excess uric acid)
Respiratory complications
Effects on respiratory function involve:
- Chronic shortness of breath
- Respiratory rhythm disorders
- Sleep apnea
- Asthma
- Dyspnea (difficulty breathing)
Digestive and skin complications
Digestive issues:
- Gastroesophageal reflux
- Gallstones
- Hiatal hernias
- Fatty liver disease, which can progress to NASH (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis)
Skin-related issues:
- Excessive sweating
- Recurrent fungal infections
- Stretch marks
- Lymphedema (swelling caused by fluid retention)
Cancer risks
Excess fat increases the risk of various cancers:
- Gynecological cancers (endometrial, breast, ovarian)
- Prostate cancer
- Digestive cancers (colon, gallbladder, liver)
Aesthetic consequences
Psychological impact
Emotional and social aspects
- Reduced self-esteem
- Exposure to weight stigma (fatphobia)
- Facing social prejudices
- Professional difficulties
Daily life impacts
- Restrictions on clothing choices
- Limited participation in social activities
- Reduced quality of life
- Potential development of social anxiety
Key point
The psychological effects are often underestimated but can be as debilitating as physical complications.
Natural solutions :
An essential foundation
Sustainable fat loss requires a holistic approach that integrates several fundamental aspects.

Free consultation
A balanced and thoughtful diet
Fundamental principle : Nutrition plays a crucial role in fat loss. Overeating can undermine all physical exercise efforts.
Effective nutritional strategies
- Moderate calorie reduction
- Choosing healthy, unprocessed foods
- Balancing macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, fats)
Specific recommendations
Managing fats
- Select healthy oils
- Incorporate avocados
- Consume fatty fish
Choosing carbohydrates
- Prioritize whole grains
- Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables
- Avoid refined sugars
The importance of fibre
- Increase soluble fibre intake
- Consume whole grains
- Promote satiety
Crucial Point
Proper hydration is essential to support the fat-loss process.
Appropriate physical activity
Strength Training
- Build muscle mass
- Increase basal metabolic rate
- Improve overall body strength
Anaerobic Activity
- Regular brisk walking
- Interval training
- Varied cardiovascular exercises
Key Success Principles
- Consistency over intensity
- Gradual progression
- Combination of different exercises
- Tailored to individual fitness levels
Stress Management and Healthy Lifestyle
Stress Management Techniques
- Regular yoga practice
- Meditation sessions
- Breathing exercises
- Daily moments of relaxation
The Importance of Sleep
- Respect natural sleep cycles
- Establish a bedtime routine
- Create a restful environment
- Ensure sufficient sleep duration
Key Advice
Consistency in these practices is more important than intensity. Gradual but sustainable habit changes yield better results than abrupt transformations.
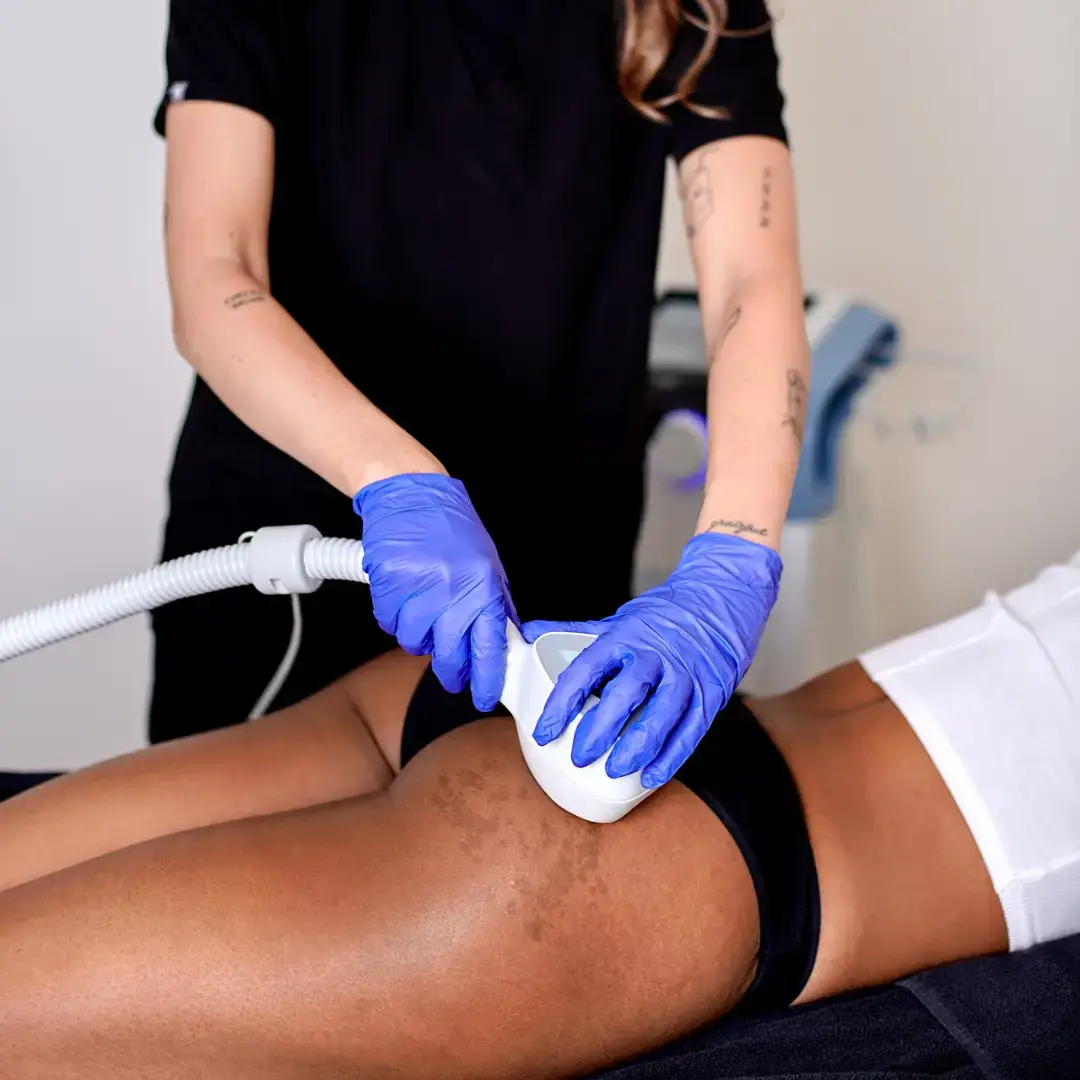
Non-invasive aesthetic treatments
Effective technological solutions
Sustainable fat loss requires a comprehensive approach that integrates several fundamental aspects.
Free consultation
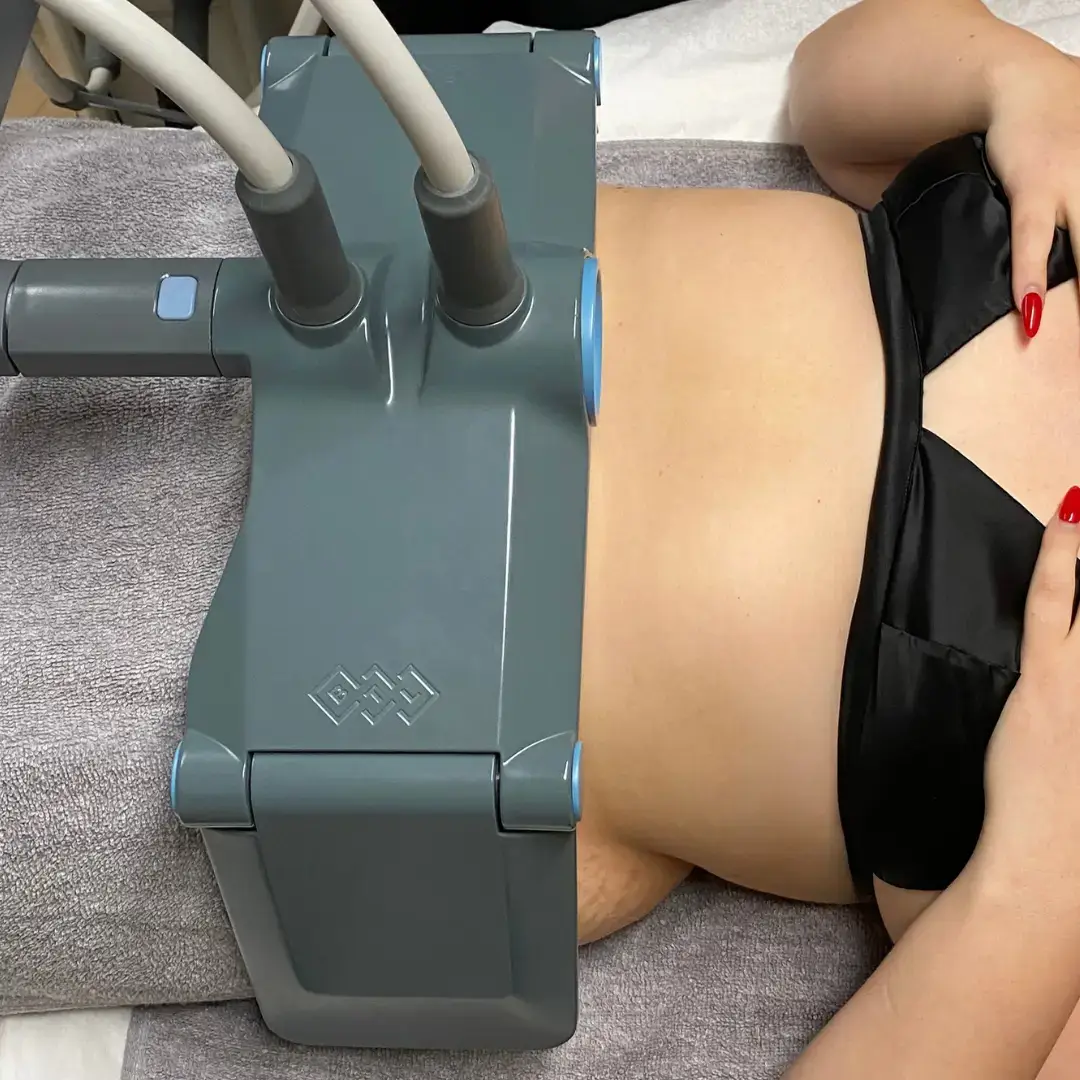
Radiofrequency
Key features :
- An ideal complement to cryolipolysis
- Targets skin laxity
- Stimulates collagen production
- Improves skin firmness
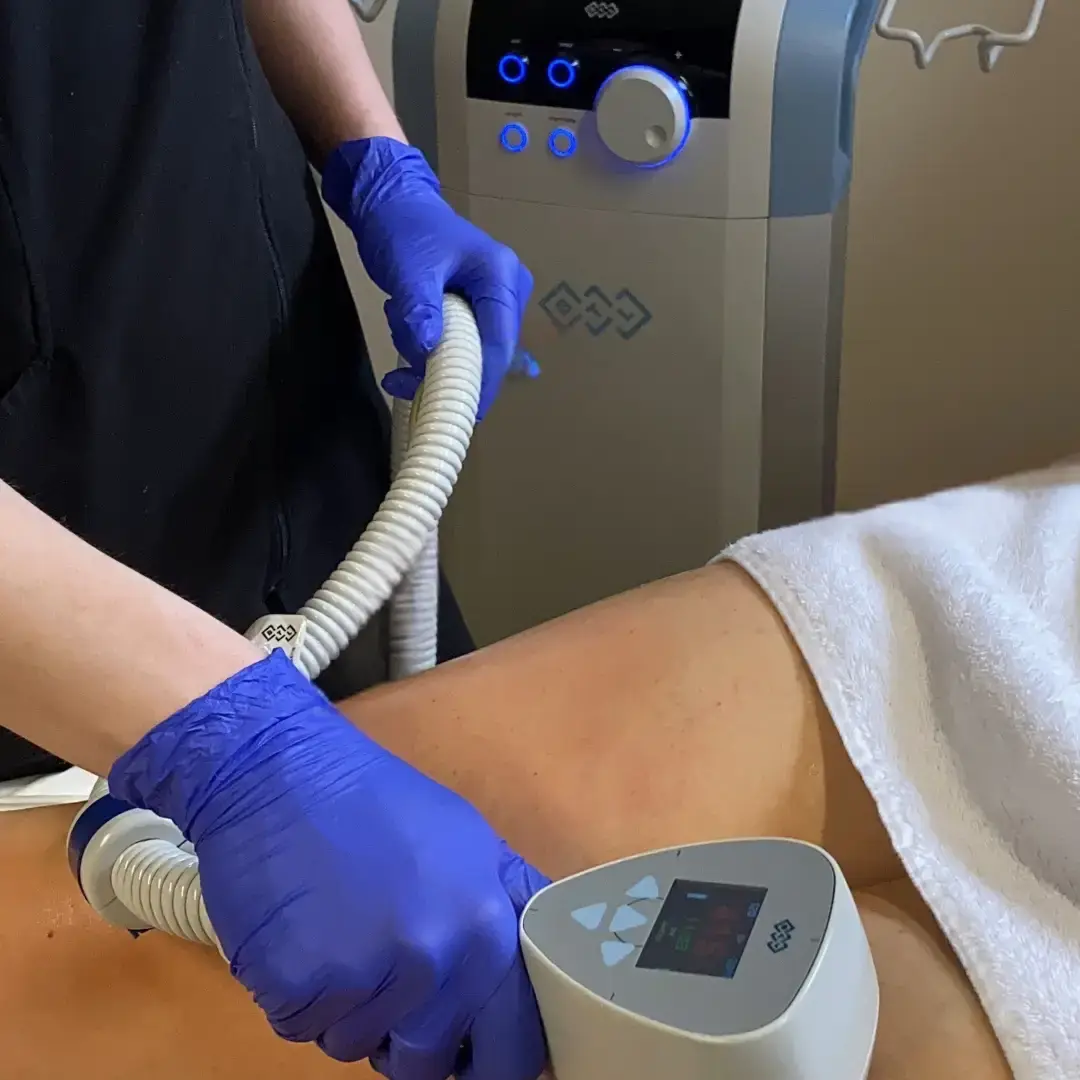
Coolsculpting (cryolipolysis)
Principes et fonctionnement : Cryolipolysis is a cutting-edge medical technique that uses controlled cooling to eliminate fat cells. This method is:
- Non-invasive
- Painless
- It is especially effective in stubborn areas
Detailed process :
- The applicator suctions the localized fat
- Intense cooling for approximately 30 minutes
- The cold damages fat cells (adipocytes)
- Apoptosis (programmed cell death) is triggered
- Natural elimination by the body
Results and effectiveness
- Visible reduction within 2–3 months
- Elimination of 30% of fat cells after the first session
- A practical alternative to liposuction
Focused ultrasound
Technology and mechanism :
This technique uses powerful ultrasonic pulses that :
- Precisely target fat deposits
- Preserve surrounding tissues (nerves, blood vessels)
- Destroy the walls of fat cells
Treatment areas :
- Thighs
- Flanks
- Abdominal region
- Double chin
Invasive aesthetic treatments
Direct and definitive solutions
Quick links
Free consultation
Liposuction
Principles and objectives
Liposuction is the gold-standard procedure for body contouring. This surgical technique offers:
- Permanent elimination of resistant fat deposits
- Precise body reshaping
- Immediate and long-lasting results
Technique and results
Lipoaspiration uses gentle techniques that enable:
- A harmonious sculpting of the face and body
- Targeted removal of fat deposits
- Sustainable transformation of body contours
Optimal candidates
The best results are achieved in patients with no significant weight fluctuations, as minimal skin laxity ensures better outcomes.
Special cases
In cases of significant weight variations, liposuction can be combined with:
- Lifting techniques
- Removal of excess tissues
- The Renuvion technique
These combinations allow simultaneous treatment of fat and skin laxity.
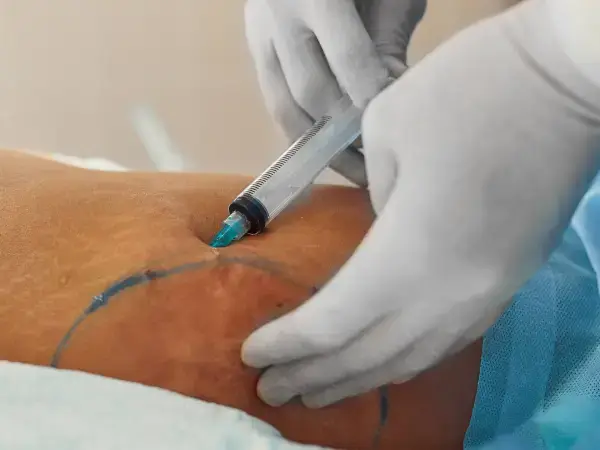
Lipolytic injections
Method description
This intermediate solution, bridging non-invasive treatments and liposuction, provides:
- Localized fat elimination
- Short, targeted sessions
- No surgery or general anesthesia is required
Treatment areas
Highly effective for:
- Saddlebag fat
- Abdomen
- Jowls
- Double chin
Specific advantages
- Gradual and natural results
- No recovery period
- Ability to treat multiple areas
- Minimally demanding procedur
Your transformation starts here
Do not hesitate to contact us for a personalized consultation and to begin your transformation.
* Results may vary from person to person. We present, to the best of our knowledge, an average of the results obtained. No guarantee is offered. Our goal is to properly evaluate your profile so that you can make an informed decision.
Réservez votre consultation
Consultation without obligation
Thousands of satisfied clients have trusted our medical-aesthetic clinic for over 15 years.
Thousands of satisfied customers




A trusted medical-aesthetic clinic for over 15 years.
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ — 4.9/5 on Google
Our commitment
Response within 24 hours
Personalized treatment
Contact Us
Phone
(438) 601-4718
Our Address
233 Av. Dunbar, Mont-Royal, QC H3P 2H4, Canada